The difference between mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia
Both mycoplasma and chlamydia belong to the broad category of bacteria, between bacteria and viruses in size, and contain both DNA and RNA. They are different from viruses because viruses have either DNA or RNA, not both. Therefore, it is classified as bacteria.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) is one of the important pathogens of respiratory tract infections, mainly causing respiratory tract infections, such as pharyngitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc., and can also cause damage to multiple organs and systems such as skin mucosa, nervous system, cardiovascular system, digestive system, and blood system. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) accounts for 10-40% of acquired pneumonia in children, and is the most common type of community-acquired pneumonia, mild MPP has a good prognosis after treatment with macrolides and other drugs, while some MPP presents severe symptoms, and some develop into critical illness. If not recognized and treated effectively in time, MPP will be treated in a more severe manner. There may be life danger or residual sequelae such as bronchitis obliterans.
Chlamydia pneumoniae (CP) is one of respiratory pathogens, can cause pneumonia, bronchus, pharyngitis, sinusitis and other acute respiratory infections. Chlamydia pneumoniae accounts for 10%-20% of community-acquired pneumonia in children and 10%-20% of adults and acute bronchitis. In fact, most chlamydia pneumoniae infections are subclinical, asymptomatic, and rarely cause significant disease, which worsens with untreated or delayed treatment.
Clinical manifestations of mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae
The onset of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is slow, with an asymptomatic period of about a week at the beginning, and then may appear: fatigue, headache, sore throat, cough (episodic dry cough, rarely pus sputum, occasionally bloodshot sputum), fever (usually moderate fever), muscle aches and so on. May be accompanied by symptoms such as wheezing, asthma-like acute attacks, nasopharyngeal pain, ear pain, etc. Symptoms of severe pneumonia: poor mental performance, refusal to eat, obvious shortness of breath, cyanosis (lips, fingers, toes, etc. Purplish blue), chest tightness, dyspnea, hemoptysis, etc. Manifestations of refractory pneumonia: After receiving regular diagnosis and treatment for a week or even longer, the symptoms still did not reduce or even worsen, such as persistent fever, severe cough, and worsening lung infection can be seen when reviewing lung imaging findings.
Chlamydia pneumoniae initially presents as sore throat, hoarseness, headache, nasal congestion, runny nose, etc., after 1-4 weeks, fever and cough (mainly dry cough) typical symptoms. Some patients in the early stage of throat swelling and pain can be improved by symptomatic treatment, 1-3 weeks after the emergence of rapid breathing, cough and other symptoms. The course of the disease is long, cough and other uncomfortable symptoms can last for 1-2 months. Chlamydia pneumoniae is more common in school-age children, and less common under the age of 3.
Complications of mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia pneumoniae
About 1/4 of confirmed patients with mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can have extrapulmonary complications, and some children have extrapulmonary symptoms that are even more obvious than respiratory symptoms, so sometimes they are prone to misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis: rash, encephalitis, hemolytic anemia, myocarditis or endocarditis, nephritis. Infection with chlamydia pneumonia, in addition to affecting the respiratory system, can also appear pulmonary symptoms: bronchial asthma, reactive arthritis, atherosclerosis, nervous system, carditis, endocarditis, pericarditis, erythema nodosum, hepatitis, thyroiditis, otitis media, etc.
Infection route and susceptible population
The infection routes of mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia pneumoniae are similar, which are transmitted through droplets or aerosols and directly invade the mucosal cells of the respiratory tract to cause respiratory tract infection. People are generally susceptible to mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia pneumoniae, but it is most common in children and adolescents over 5 years old. Infection can occur throughout the year, generally in schools, nursing homes, hospitals and other densely populated places prone to cluster infection.
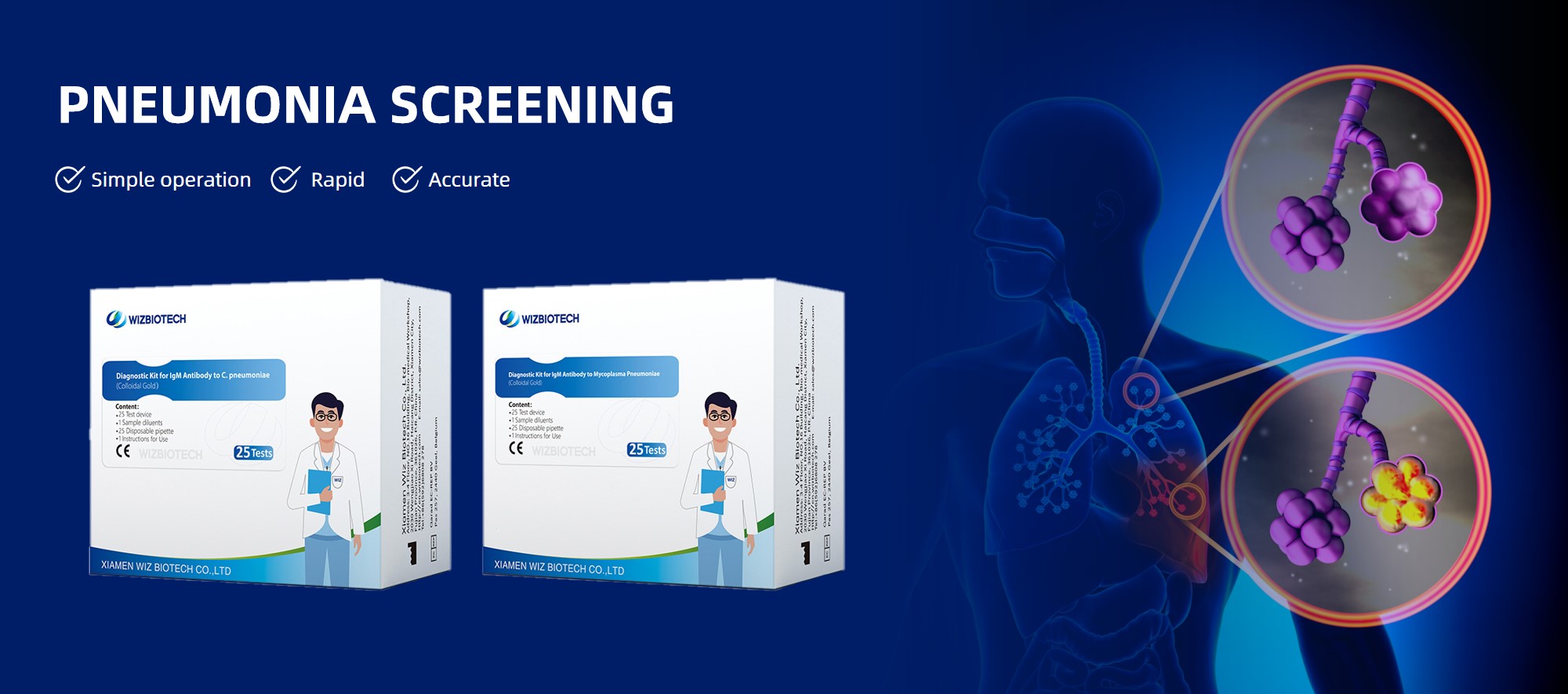
WIZ has independently developed Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM antibody test kit (colloidal gold method) and Chlamydia pneumoniae IgM antibody test kit (colloidal gold method), which can be used for rapid detection of mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia pneumoniae infection, helping doctors to carry out early diagnosis and treatment, and improving the treatment effect and prognosis of patients. Welcome the hospital purchasing department and related institutions to consult and place orders, we will provide the best quality medical services for your hospital to provide better support and help. We look forward to working with you.