[Literature Sharing] Changes of WBC and CRP levels in children co-infected with mycoplasma pneumoniae and influenza virus
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a common pathogen that causes pneumonia in children. Harmful substances produced by its metabolism can aggravate cell damage and cause a variety of complications.
Clinically, the co-infection of influenza virus and mycoplasma in children can lead to muscle soreness, high fever, cough, fatigue, etc., and death in severe cases, so the early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
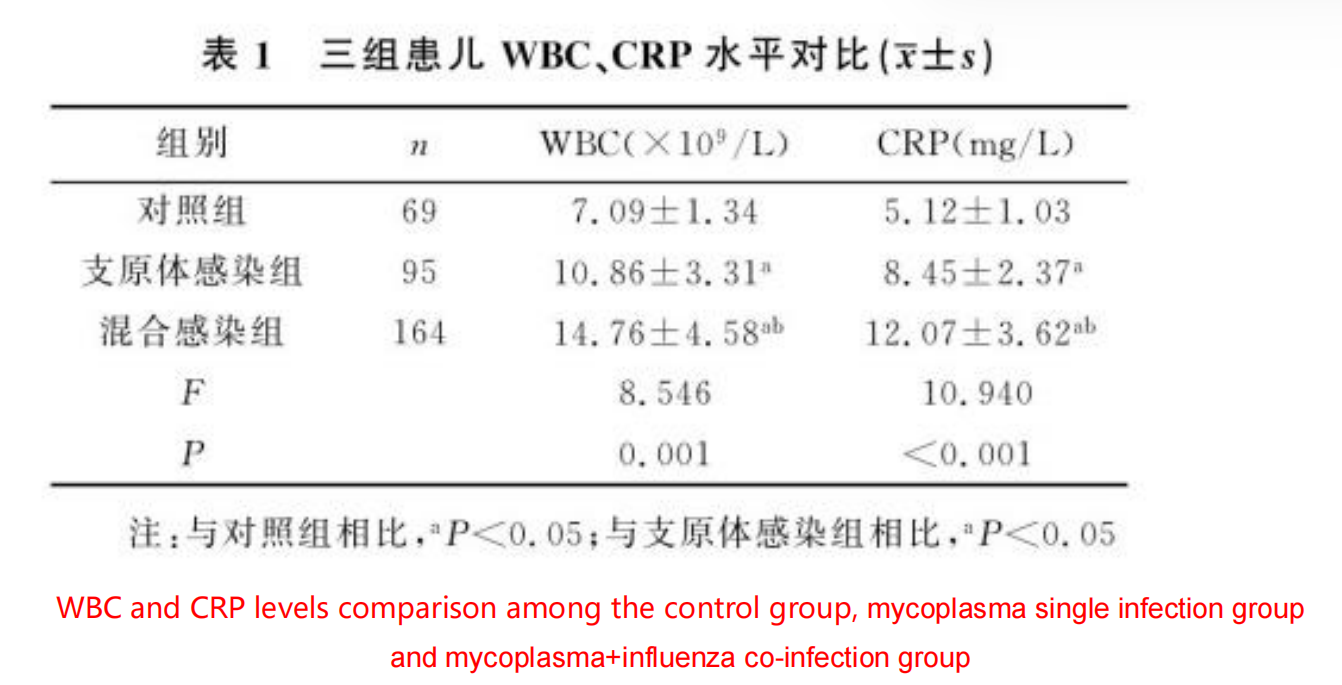
Recently, some researchers have monitored and analyzed the relevant indicators of children with co-infection of mycoplasma pneumoniae and influenza virus. Through the observation of the changes of white blood cell count (WBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in these children, it was found that the WBC and CRP levels were higher in children with co-infection of mycoplasma pneumoniae and influenza virus and the increase of WBC and CRP levels increased with the extension of admission time, and the levels of WBC and CRP were the highest on the 3rd day after admission. The diagnostic value of combined detection is higher in children co-infected with mycoplasma pneumoniae and influenza virus.

Firstly, the study found that WBC levels were generally higher in these children. Children with co-infection had significantly higher WBC than those with a single infection of the influenza virus or mycoplasma pneumoniae. The WBC is an important part of the body's immune system, primarily responsible for defending against foreign pathogens. When the body is infected by a virus or bacteria, the number of white blood cells increases rapidly to boost immune function and and clear pathogens better.
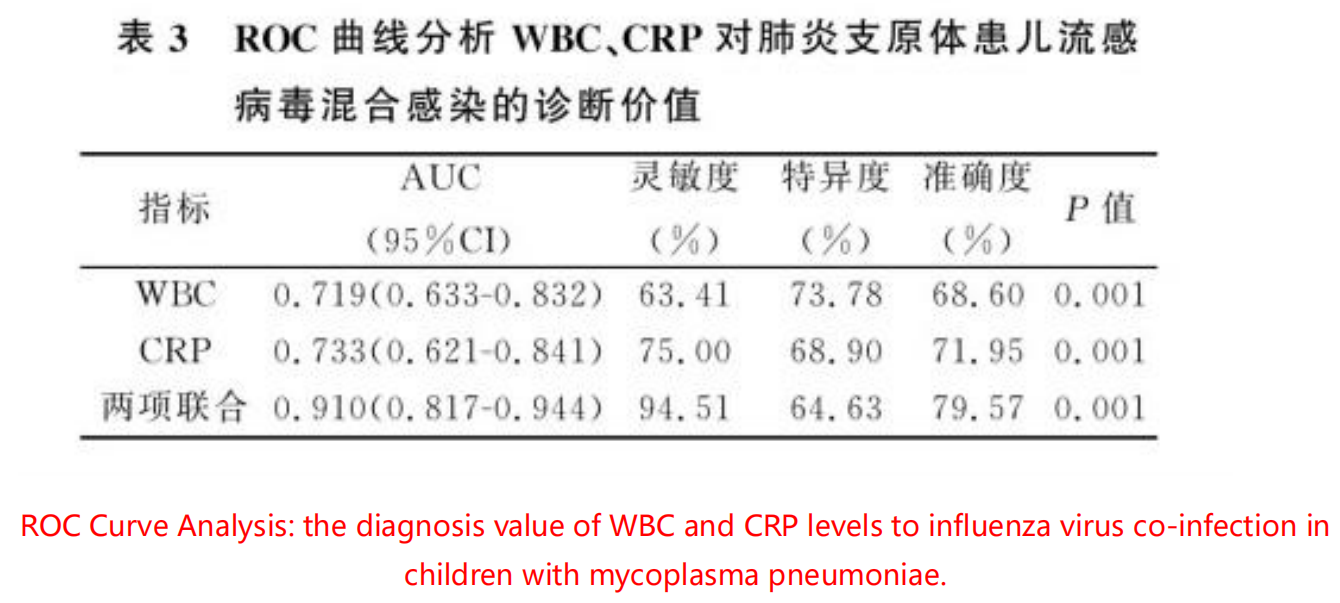
When mycoplasma single infection, WBC level is mostly in the normal range, while co-infection will cause a large increase in blood WBC, and the continuous rise of WBC level will also lead to poor prognosis of children.The research indicates the AUC value of WBC for the diagnosis of influenza virus co-infection in children with mycoplasma pneumoniae was 0.719, indicating that WBC could be used as a predictor of influenza virus co-infection in children with mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Secondly, CRP level also showed certain characteristics. CRP is an acute response protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation. Study have found that CRP levels are elevated in children with co-infections and that persistently elevated CRP levels can affect patient prognosis.
Combined with previous studies, it can be concluded that the change of CRP level can play a guiding role in the treatment of infected children. The increase of CRP level is not obvious in viral infection, but the increase of CRP level in children indicates the possibility of co-infection with mycoplasma infection and appropriate antibiotics should be considered. The sensitivity of the combined detection of WBC and CRP was 91.06, which was better than that of the independent detection.
In conclusion, the combined infection of mycoplasma pneumoniae and influenza virus can significantly increase the levels of WBC and CRP inchildren. This may be due to the two pathogens working together to trigger a stronger immune and inflammatory response. For clinicians, close monitoring of the changes of WBP and CRP in these children is helpful to detect the illness changes in time, and improve the evaluation efficiency of early diagnosis and treatment of disease.
At the same time, it also suggests that for patients infected with multiple pathogens at the same time, the disease may be more complex and the prognosis is more difficult to predict. Therefore, in the process of diagnosis and treatment, clinicians need to evaluate patients' conditions more carefully and comprehensively, and formulate personalized treatment plans. Only in this way can the therapeutic effect be maximized and the risk of complications be reduced.