The Gastric Cancer Screening and Early Diagnosis and early Treatment Program (2024 edition) was released
According to the latest data from the National Cancer Center, there were 358,700 new cases of gastric cancer in China and 260,400 deaths in 2022. The incidence of malignant tumors ranked fifth in China, and the mortality rate ranked third. It seriously threatens people's lives and health and becomes a major public health problem in our country. The prevention and treatment of gastric cancer is a major challenge in the prevention and control of malignant tumors in China. In June, the Department of Medical Emergency Response of China issued the "Gastric Cancer Screening and Early Diagnosis and Treatment Program" (hereinafter referred to as the program) formulated by the National Health Commission, which further standardized the work related to gastric cancer screening and early diagnosis from the aspects of epidemiology, risk groups, screening, early diagnosis and treatment principles, follow-up management, etc., to improve the prevention and treatment effect of gastric cancer.
As mentioned in the gastric cancer screening and early diagnosis and early treatment program, the main risk factors for gastric cancer include Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection, specific dietary habits, poor lifestyle, related medical history and genetic factors. Insufficient screening of Hp and gastric cancer is the key factor for the high incidence of gastric cancer in China. Relevant data show that the current Hp infection rate in China is 50% to 56%, and about 700 million people are infected. Over the past 60 years, the incidence of stomach cancer has gradually declined in Western Europe and North America, due in part to the reduction of the risk of stomach cancer due to the control of Hp transmission by meal-sharing. In addition to the reduction of risk factors for gastric cancer and the improvement of living habits, gastric cancer screening has become one of the effective methods for high-risk groups of gastric cancer. According to statistics, the median overall survival time of gastric cancer patients is only 16 months, in order to extend the 5-year survival rate of patients, early detection and early treatment is undoubtedly the key to solve the problem. Screening for gastrointestinal cancer is the most effective way to reduce the incidence and mortality of gastrointestinal cancer. Through screening, early detection, early intervention and early treatment, the development of the disease can be blocked, the mortality rate can be reduced, and the economic burden of residents can be reduced.
How to test?
The recommended screening objects are: people at high risk of gastric cancer (FIG. 1), with no history of digestive tract, aged between 4 and 74 years, without contraindications for endoscopy, and able to cooperate with endoscopy.

Figure 1:High risk group of gastric cancer
In the protocol, endoscopy is recommended as the first screening method, and it is not recommended to detect serum pepsinogen (PG), serum gastrin-17 (G-17) or serum gastric cancer-related antigen MG7 alone.
Although gastroscopy is highly accurate in the early diagnosis of gastric cancer, it is difficult to be applied to large-scale gastric cancer screening due to its high invasion, high cost, insufficient medical resources and other problems.
As for the "PG and G-17 are not recommended for gastric cancer screening alone" mentioned in the gastric cancer screening and early diagnosis and early treatment program, does it mean that these biomarkers PG and G-17 are not suitable for gastric cancer screening?
In fact, according to the results of previous studies, the accuracy and reliability of using serum indicators alone for gastric cancer screening is indeed not high. Combined with the recommendations of multiple guidelines in the past, screening with PG, G-17 and Hp serological markers can more effectively screen out high-risk groups of stomach diseases. Then, targeted gastroscopy for high-risk groups is a more feasible and effective screening strategy. This combined screening strategy can integrate the information of multiple indicators, improve the accuracy and reliability of screening, and help early detection of individuals with gastric cancer or gastric precancerous lesions, so as to take timely intervention and treatment measures.
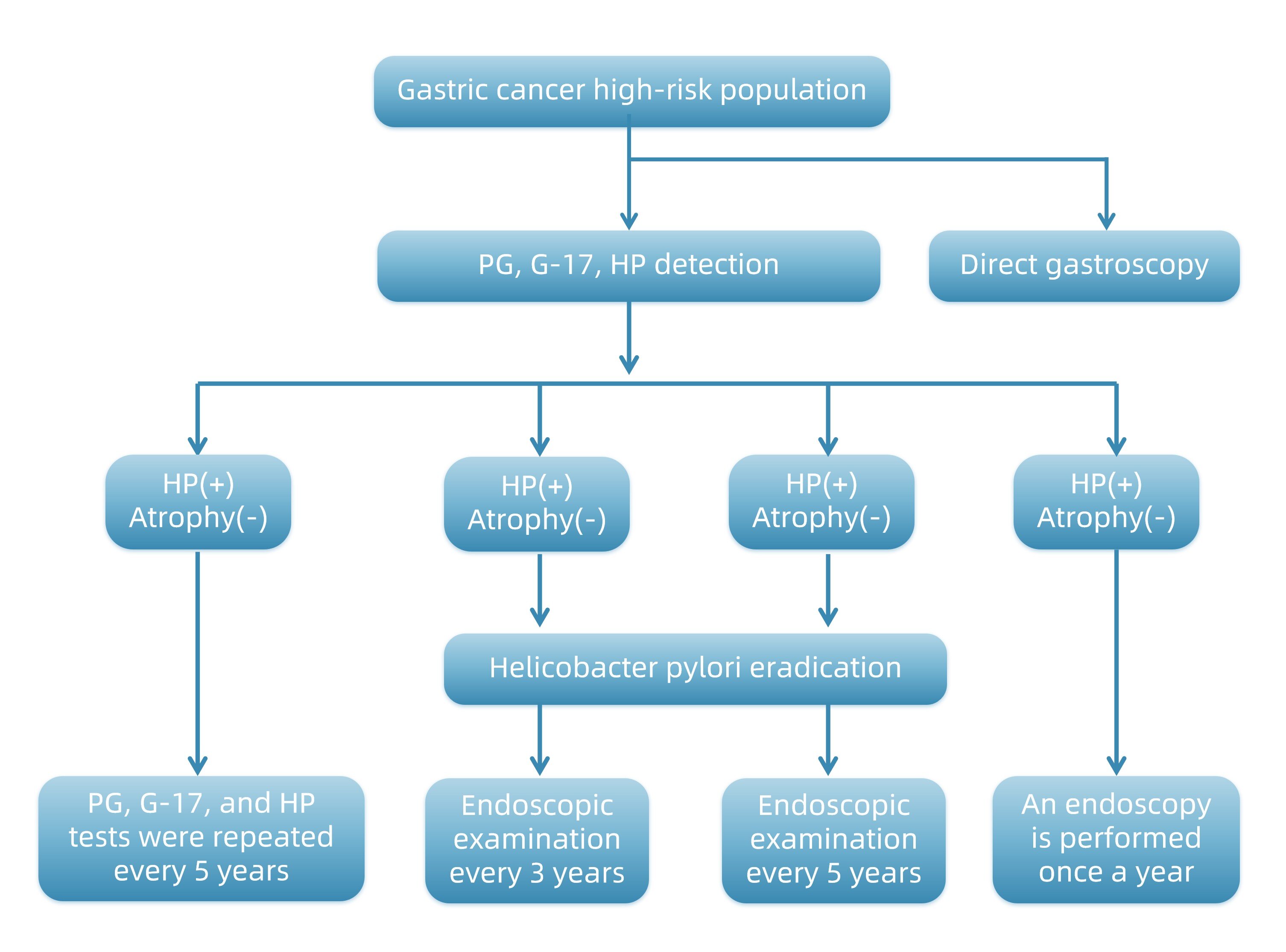
Figure 2:Gastric cancer screening method
Refer to the Chinese Expert Consensus on Early Diagnosis and Early Treatment of Gastric Cancer (2023 edition)
Wizbiotech offers a gastric cancer early screening solution that combines the PG, G-17 and Hp indicators for a more accurate assessment of an individual's stomach cancer risk. PG is a protein secreted by gastric mucosa cells, and its level can reflect the secretion of gastric acid; G-17 is a gastrin, and its level can reflect the secretion of gastric acid; Hp is helicobacter pylori, which is a major pathogenic factor leading to gastric cancer.
By combining these three indicators, a more comprehensive understanding of an individual's stomach health can be obtained, including but not limited to gastric cancer, superficial gastritis, atrophic gastritis, and gastric ulcers. The characteristics of this gastric cancer early screening solution are simple, convenient, comprehensive and accurate, which can help high-risk groups to carry out hierarchical prevention and control, alleviate the shortage of gastroscopy resources, optimize the allocation of medical resources, save the trouble of repeated testing and avoid unnecessary gastroscopy for some patients.
Wizbiotech's gastric cancer screening solutions are dedicated to helping each individual better understand their stomach health and intervene to prevent disease from occurring. Through scientific detection and analysis, the most suitable prevention and treatment programs are provided for everyone, so that everyone can enjoy a healthy life. If you need to learn more about our solutions and order our products, you can contact our sales.