Summer is coming, beware of dengue fever
As of April 30, 2024, more than 7.6 million dengue cases have been reported globally, including 3.4 million confirmed cases, more than 16,000 severe cases, and more than 3,000 deaths. Although the number of dengue cases has increased significantly globally over the past five years, the increase has been particularly significant in the Americas region. By the end of April 2024, the number of cases in the Americas region has exceeded 7 million, surpassing the 4.6 million cases in 2023.
Currently, 90 countries are known to be experiencing active dengue transmission in 2024, but not all have officially reported it. In addition, many endemic countries lack effective detection and reporting mechanisms, leading to an underestimation of the global burden of dengue. To control transmission more effectively, real-time, robust dengue surveillance is needed to address undetected cases, co-transmission with other arboviruses, and misdiagnosis. These factors can contribute to unrecognized disease transmission and identify the risk of local transmission in potentially non-endemic countries.
Dengue virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female mosquitoes, mainly Aedes aegypti. Other Aedes species can also act as vectors, but the impact is usually inferior to Aedes aegypti. However, in 2023, Europe saw a surge in local transmission of dengue caused by Aedes albopictus (tiger mosquito).
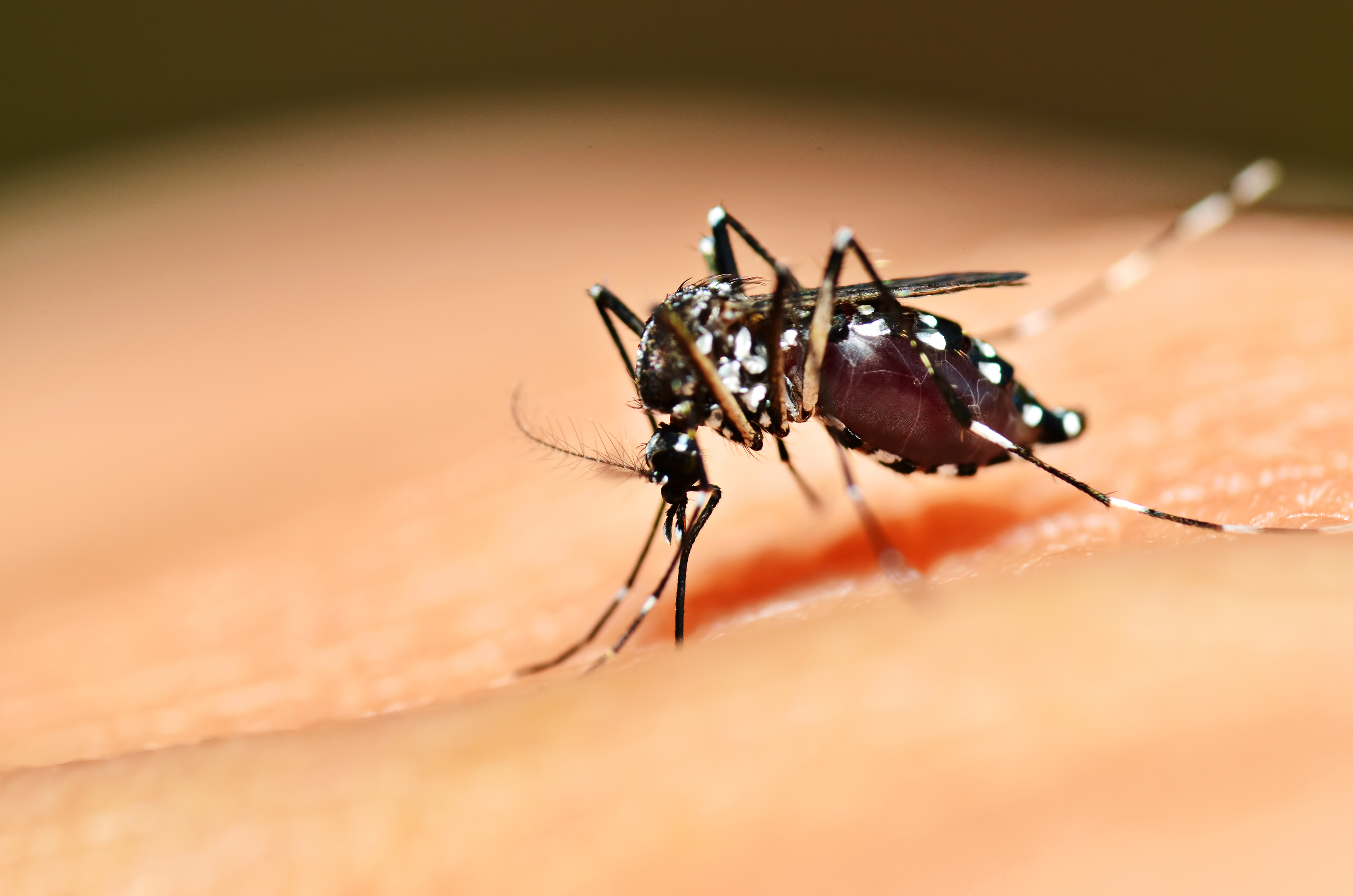

After feeding on the blood of an infected person, the virus replicates in the midgut of the mosquito and then spreads to secondary tissues, including the salivary glands. The time it takes from ingesting the virus to actually spreading it to a new host is called the incubation period. When the ambient temperature is between 25-28°C, the incubation period takes about 8-12 days. The variation of the incubation period is not only affected by the ambient temperature, but also by the daily temperature fluctuation range and virus genotype. After infection, mosquitoes can spread the virus for the rest of their lives.
After the dengue virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito, cases are mostly asymptomatic or lead to a mild febrile illness. However, some cases may progress to severe dengue involving shock, severe bleeding or organ damage. Once infected in humans, it can be transmitted from mother to child and through blood.
People can protect themselves from mosquito bites and reduce their risk of dengue fever as much as possible by:
Wear as much clothing as possible to cover your body;
Use bed nets during the day, preferably those sprayed with insect repellent;
Use window screens;
Use mosquito repellents (including DEET, pecaridin or IR3535);
Use mosquito repellent incense and spray repellents
Prevent mosquitoes from entering spawning habitats through environmental management and management measures;
Proper disposal of solid waste and removal of man-made habitats containing water;
Cover household water storage containers and empty and clean them weekly;
Apply appropriate insecticides to outdoor water storage containers.
Reliable and effective surveillance is an important means to stop transmission and receive timely treatment. WIZ offers dengue IgG/IgM antibody test kits (colloidal gold)with high sensitivity and specificity. When IgM antibody is positive, it indicates the acute phase of primary or secondary infection with dengue virus. When the IgG antibody is positive, it indicates that it has been infected with Dengue virus or has been infected with Dengue virus again. When both IgM and IgG antibodies are positive, it indicates that the primary infection is late or the secondary infection is early. If you need to order our products, you can contact our sales.