Main respiratory pathogens and detection methhods
Main respiratory pathogens and detection methods
一,The main respiratory pathogens?
1. Viruses
1)Influenza virus: belongs to orthomyxovirus family, divided into A, B, C three types, of which A and B are more common. Influenza A virus is prone to mutation, can be further divided into H1N1, H3N2, H5N1, H7N9 and other subtypes.
The incubation period is short, usually 1 to 3 days.
2)Respiratory syncytial virus: belongs to paramyxoviridae, has only one serotype. Infants and children are generally susceptible, the human body can not produce permanent, specific antibodies after infection, so repeated infection may occur.
3)Parainfluenza virus: belongs to the paramyxovirus family, is a respiratory virus that causes mild influenza-like symptoms, the population is generally susceptible, infants are prone to lower respiratory tract infection. The incubation period is 2 to 5 days.
4)Adenovirus: belongs to the adenovirus family, the population is generally susceptible, people of all ages can be infected with adenovirus, but infants, the elderly and immunocompromised people, young adults and medical staff are more susceptible.
The incubation period is generally 3 to 10 days.
5)Coxsackie virus: It is an enterovirus, divided into two types A and B, which can infect the human body through the digestive tract and respiratory tract. Human infection with coxsackie virus is easy to cause herpetic angina and non-paralytic poliomyelitis and other changes. The incubation period is generally 1 to 3 days.
6) SARS-COV-2: A beta coronavirus, there are a variety of variant strains, the population is generally susceptible. The incubation period of most patients infected with the novel coronavirus is 3 to 7 days, and the incubation period of individual patients is longer, up to 14 days.
2. Bacteria:
1) Streptococcus pneumoniae: It is one of the main pathogens of pneumonia and can also cause other respiratory infections and blood infections.
2) Klebsiella pneumoniae: Commonly causes pneumonia and urinary tract infections, and some strains may become resistant to antibiotics.
3) Haemophilus influenzae: It is a common pathogen of respiratory infections, especially in children.
4) Legionella pneumophila: can cause severe pneumonia, mainly through water transmission.
3. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae
1) Mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia pneumoniae are microorganisms between bacteria and viruses. They are common pathogens that cause acute respiratory infections in adolescents. The incubation period is long, usually 2 to 4 weeks.
二,Two, how to detect different types of pathogens?
The detection of pathogens is essential for early diagnosis, treatment and control of the spread of diseases. At present, pathogen detection mainly includes: antigen detection, antibody detection and nucleic acid detection.
1. Antigen detection: Confirm the type of infection by testing a sample for pathogen specific antigens. This method is simple and fast, and the specimen type is often nasopharyngeal swab or oropharyngeal swab, which is suitable for early screening of acute infection and convenient for self-testing at home. However, the sensitivity of antigen detection is relatively low.
2. Antibody detection: Confirm a past or present infection by testing the level of specific antibodies produced in the body's blood. Clinically, two types of specific IgM and IgG antibodies are mainly tested.
1) IgM is the earliest antibody, generally appearing about 1 week after infection, reaching a peak about 2 to 4 weeks and gradually decreasing after a short maintenance time, therefore, pathogen specific IgM detection can be used for the early diagnosis of acute infection or infectious disease.
2) IgG-type antibodies appear later than IgM, but last longer and usually indicate past infection or are used for population epidemiological investigation. Clinically, two serum samples can be combined with the dynamic change of antibody content to detect the level of pathogen-specific IgG antibodies. The first sample should be collected as soon as possible at the beginning of the disease (acute phase), and the second sample should be collected 2 to 3 weeks later (recovery phase). If the titer of specific IgG antibodies in the second sample is more than 4 times that of the first sample, It is also of great diagnostic value for acute infectious diseases. It should be reminded that there is a false negative or false positive possibility of antibody detection, which should be combined with clinical comprehensive analysis.
3. Nucleic acid testing: The infection is confirmed by analyzing the nucleic acid sequence of the pathogen. The main types of specimens for respiratory infections are nasopharyngeal swabs, oropharyngeal swabs, sputum specimens, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. This method has strong specificity, high sensitivity and high accuracy, especially in the case of early infection or low viral load, and has good clinical value. However, nucleic acid detection usually has high requirements on testing equipment, personnel qualifications and laboratory conditions, and the detection time is relatively long.
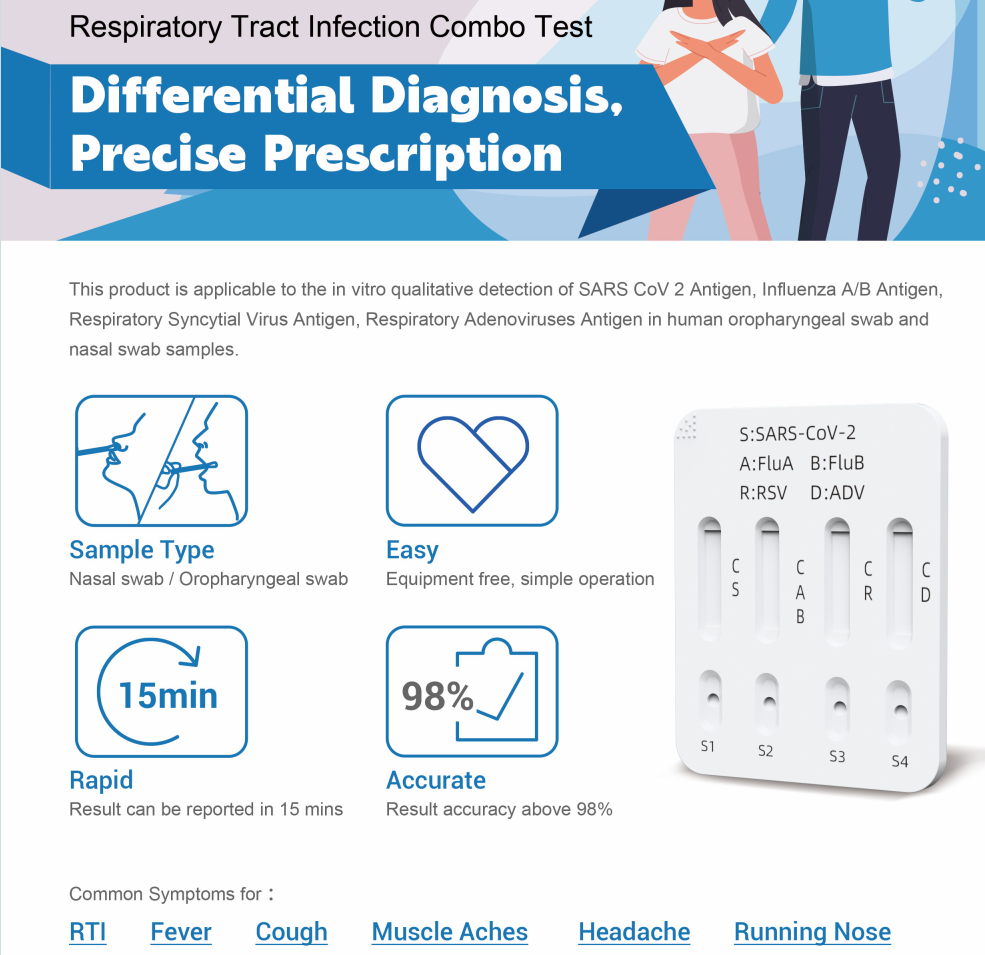
3. WIZ Repiratory Tract Infection Combo Test: