Four tests of gastric function - the best early screening method for gastric cancer!1
The four tests of gastric function are the first choice screening means for early prevention, early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment of gastric cancer. The test mainly includes serum pepsinogen I(PGI), serum pepsinogen II(PGII), ratio of serum pepsinogen I to serum pepsinogen II(PGI \PGII), serum gastrin 17(G-17) and antibodies to Helicobacter pylori (HP).
(1) Serum pepsinogen (PGI, PGII)
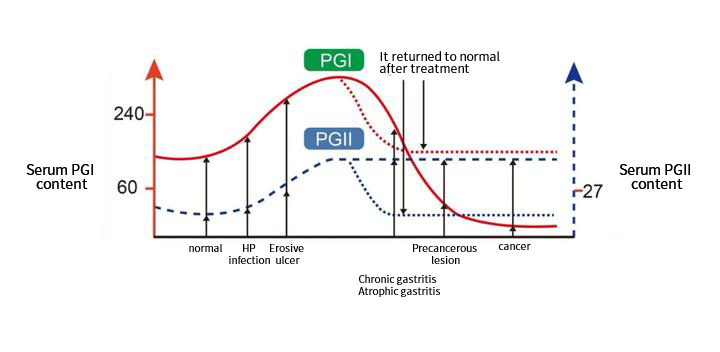
Pepsinogen (PG), the precursor of pepsin, is divided into two subgroups according to its distribution and immunogenicity: pepsinogen I(PGI) and pepsinogen II (PGII). PGI and PGII are proteins secreted by gastric mucosal cells. About 1% of pepsinogen enters the bloodstream and remains stable. When the stomach atrophies, the secretion of pepsinogen is changed. Therefore, serum PGI and PGII levels can be used as reliable indicators of gastric mucosa atrophy. At present, pepsinogen level testing has been considered to be the "serological gastroscopy test". Pepsinogen detection is the most suitable for health examination, often can find peptic ulcer, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer and other gastric diseases, and it is of great significance for the early diagnosis of gastric diseases and the prevention and intervention of gastric cancer.
(2) Serum gastrin 17(G-17)
Gastrin is a gastrointestinal hormone mainly secreted by the G cells of the antrum and duodenum, which plays an important role in regulating the function of the digestive tract and maintaining its structural integrity. More than 95% of the bioactive gastrin in the human body is alpha-aminated gastrin, which mainly contains two isomers G-17 and G-34, of which 80%-90% is G-17. G-17 is only secreted by G cells in gastric antrum, so G-17 is an important indicator to reflect the damage of gastric mucosa.
(3) Helicobacter pylori Antibody (HP)
Helicobacter pylori is a stubborn bacteria, often living in the human stomach and duodenum, it can not only cause gastritis, gastric ulcer and other digestive system diseases, but also closely related to the occurrence of gastric cancer. Studies have shown that Helicobacter pylori can induce abnormal cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis through various ways, thus promoting the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. Therefore, Helicobacter pylori antibody detection is also an essential indicator for gastric cancer screening.
The four tests for gastric function are performed outside the body by taking a blood sample from the patient and are non-invasive and painless. It takes about two hours on an empty stomach before the sample is taken. Through rigorous and scientific data ratio calculation, the examination can accurately reflect whether it has entered the risk range of severe lesions or even cancer. The disease with unknown symptoms can be grasped very accurately, and the possibility of recurrence can be accurately detected according to the data.
Clinical significance of four tests of gastric function
PGI is mainly secreted by gastrine gland cells and is an indicator to detect the function of gastrine gland cells. PGII is produced by gastric cardia gland, pyloric gland and proximal duodenal Brunner gland in gastric antrum, and is closely related to gastric fundus mucosal lesions. The change of PGI/PGII ratio can reflect the degree of gastric mucosa atrophy. Serum PGI and PGII can not only reflect the number of gastric mucosal glands and cells, but also indirectly reflect the secretion function of different parts of gastric mucosa. It is not affected by diet, has no day and night and seasonal changes, and can be used as a means to monitor the state of gastric mucosa and make up for the blank area of gastric function detection. PGI and PGII levels were positively correlated with Helicobacter pylori infection, and could be used as an evaluation index of eradication treatment effect. Pepsinogen can be used as an indicator of peptic ulcer recurrence: PGI increased significantly in patients with early gastric ulcer and PGII increased significantly in patients with recurrence. The serum PG level of patients after gastric cancer resection was significantly lower than that before operation, and PGI and PGII were increased in patients with recurrent gastric cancer.
G-17 can reflect the atrophic condition of gastric antrum mucosa, and its level depends on the gastric acidity and the number of G cells in the antrum. Clinically, it is used to indicate the functional status of gastric mucosa in patients, and to assist the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcer and other diseases. Serum G-17 concentration was lower in patients with high gastric acid and antral atrophy. In combination with serum PG testing, serum G-17 concentration testing can be used to diagnose atrophic gastritis in the antrum (reduced G-17 levels) or confined to the body of the stomach (elevated G-17). Combined detection of serum PG, PGI/II and G-17 can improve the accuracy of assessing the extent and degree of gastric mucosa atrophy.
Gastric cancer screening methods recommended
Upper gastrointestinal barium meal angiography can detect part of early gastric cancer, which is often carried out in Japan. However, due to the inability to biopsy and the presence of radiation, the sensitivity and specificity are not high, and it has been replaced by endoscopy, so it is not recommended to use X-ray barium meal for gastric cancer screening. Endoscopy and endoscopic biopsy are currently the gold standard for the diagnosis of gastric cancer. In recent years, painless gastroscopy has developed rapidly and has been applied to endoscopic screening of high-risk groups of gastric cancer, which has greatly improved the acceptance of patients with gastroscopy. However, the examination price of this item and a series of preparations before examination are still common reasons for patients to refuse examination. The new version of the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer was released in 2022, and it is recommended that the risk of gastric cancer can be stratified by four tests of serum gastric function, and further examination strategies can be determined. This can avoid unnecessary gastroscopy for some patients, save patient costs, and promote the effectiveness of medical resource allocation to a greater extent.
Wizbiotech offers an early screening solution for gastric cancer at a competitive price. At the same time, the program only needs to collect one tube of blood, and can complete the detection work of four items within 15 minutes to realize the screening of stomach diseases, including but not limited to gastric cancer, superficial gastritis, atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, etc. Its convenient sampling, clear clinical significance, can well help doctors to understand the stomach condition of patients, all levels of hospitals are applicable. All these products have obtained CE certification and have been sold to many European countries, and have been recognized and trusted by all partners. We sincerely welcome hospitals and major distributors to purchase, please contact us on the official website of Wizbiotech.